WaiPRACTICE

WaiPRACTICE August 2020
View the Project on GitHub women-in-ai-ireland/August-2020-WaiLEARN-QA-Chatbot
Contributors
Monsurat Oluwatosin | LinkedIn|GitHub Bhakti Chauhan | LinkedIn|GitHub Pallavi Kale | LinkedIn|GitHub Onyinye Chudi-Iwueze | LinkedIn|GitHub
This project describes a QA Chatbot built using the Facebook Babi Dataset.
What is a Chatbot?
A Chatbot is a computer program that facilitates technological and human communication through various input methods, such as text, voice and gesture. Chatbots serve the purpose of digital assistants, virtual assistants, AI assistants and much more. The recent technological advancement like Natural Language Processing(NLP), Artificial Intelligence(AI), Data Mining and Machine Learning(ML) have resulted in the creation of advanced AI Chatbots that are useful to businesses and individuals alike.
Chatbot Functionality
Chatbot is used by enterprises to communicate within their business, with customers regarding the services rendered and so on. The Chatbot understands text by using Natural Language Processing (NLP). Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is used by chatbots to understand the language, which is combined with algorithms to give a suitable response to the supplied query. The next level in the delivery of the natural and personalized experience is achieved by Natural Language Generation (NLG).
Types of Technology for Chatbots
The technology driving today’s chatbot is linguistics and machine learning. The linguistic chatbots are also known as rule based chatbots and are structured in a way that responses to queries are done in meaningful ways. These chatbots are basic and close to interactive questioning. Machine learning (AI chatbots) are complex chatbots which are data driven and use NLU to personalize answers.
How are chatbots trained?
To train AI bots, it is paramount that a huge amount of training data is fed into the system to get sophisticated services. A hybrid approach is the best solution to enterprises looking for complex chatbots. The queries which cannot be answered by AI bots can be taken care of by linguistic chatbots. The data resulting from these basic bots can then be further applied to train AI bots, resulting in the hybrid bot system.
The Facebook bAbI dataset
The bAbI project was conducted by Facebook AI research team in 2015 to solve the problem of automatic text understanding and reasoning in an intelligent dialogue agent. To make the conversation with the interface as human as possible the team developed proxy tasks that evaluate reading comprehension via question answering. The tasks are designed to measure directly how well language models can exploit wider linguistic context. For our project, the subset of Babi Data Set from Facebook Research is used. Read more about bAbi here.
We will be developing a simple chatbot that can answer questions based on a “story” given to it. So without any further ado let’s get started!
Step 1: Import required libraries and read the data files.
Python pickle module is used for serializing and de-serializing a Python object structure. The numpy library is used to work with arrays. We will unpickle train and test data.
import pickle
import numpy as np
# Keras library imports for tokenization and model building
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.layers.embeddings import Embedding
from keras.layers import Input, Activation, Dense, Permute, Dropout
from keras.layers import add, dot, concatenate
from keras.layers import LSTM
Step 2: Data Exploration
As we can see, the type of train and test data is list. The length of train and test data is 10000 and 1000 respectively. The data has stories, questions and answers.
type(test_data)
# list
type(train_data)
# list
len(test_data)
# 1000
len(train_data)
# 1000
Step 3: Setting up vocabulary of all words.
A vocabulary dictionary is set up to hold the vocab words.
vocab = set()
all_data = test_data + train_data
for story, question , answer in all_data:
vocab = vocab.union(set(story))
vocab = vocab.union(set(question))
Step 4: Vectorizing the data
We would be using Keras library for processing this vocab. Keras is an open source neural network library written in Python. It could run on top of TensorFlow, Theano, Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit, R. TensorFlow is a machine learning tool which is designed for deep neural network models. Pad_sequences in Keras is used to ensure that all sequences in a list have the same length. By default this is done by padding 0 in the beginning of each sequence until each sequence has the same length as the longest sequence. Keras provides the Tokenizer class for preparing text documents. The Tokenzier is constructed and is fit on the text documents using fit_on_texts . After the fit, Tokenzier allows us to use word_index (A dictionary of words and their uniquely assigned integers) on the documents. Each token(word) in the story is assigned an integer. We can then check the length of training data story text and length of story sequence.
We can just put everything into one function as shown below:
def vectorize_stories(data, word_index=tokenizer.word_index,
max_story_len=max_story_len,max_question_len=max_question_len):
# X = STORIES
X = []
# Xq = QUERY/QUESTION
Xq = []
# Y = CORRECT ANSWER
Y = []
for story, query, answer in data:
x = [word_index[word.lower()] for word in story]
xq = [word_index[word.lower()] for word in query]
y = np.zeros(len(word_index) + 1)
y[word_index[answer]] = 1
X.append(x)
Xq.append(xq)
Y.append(y)
# RETURN TUPLE FOR UNPACKING
return (pad_sequences(X, maxlen=max_story_len),pad_sequences(Xq, maxlen=max_question_len), np.array(Y))
This function will take input data that contains stories, queries and answers, a word_index which is a dictionary of words and assigns integers, maximum length of story and longest question as parameters. The function vectorized the stories,questions and answers into padded sequences. A loop runs through every story,query and answer and the raw words are converted into a word index. Each set of story, query and answer is appended to their output list. The aforementioned words are tokenized to integers and the sequence is padded so that each list is of equal length. This is in the form of a tuple.
We can see how the input data from the test is vectorized by calling the function.
Step 5: Creating the model
We used Python Keras Sequential model which is a linear stack of models. Encoder is a stack of recurrent units in which each element takes a single element of the input sequence, gathers information and passes it forward (encoder vector). In the facebook bAbI question- answering , the input sequence is a word in the question. The inputs get embedded into a sequence of vectors. Encoder vector encapsulates the information from input elements so that the decoder can make accurate predictions. It’s a hidden state of the decoder part of the model. Decoder is a stack of recurrent units in which each predicts an output at a time step t. Read more about the model here.
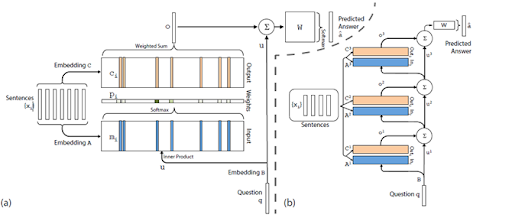
Step 6: Evaluating the Model
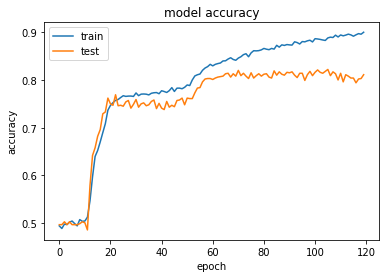
We plot the model accuracy using the matplotlib library. In terms of artificial neural networks, an epoch refers to one cycle through the full training dataset. The visualisation plot shows the training and test accuracy of the mode across 120 epochs.
Step 7: Test Results
After model building we can check some of the test stories and see the performance of the model in predicting the right answer to the query.
story =' '.join(word for word in test_data[0][0])
print(story)
# Mary got the milk there . John moved to the bedroom
query = ' '.join(word for word in test_data[0][1])
print(query)
# Is John in the kitchen ?
print("True Test Answer from Data is:",test_data[0][2])
# True Test Answer from Data is: no
#Generate prediction from model
val_max = np.argmax(pred_results[0])
for key, val in tokenizer.word_index.items():
if val == val_max:
k = key
print("Predicted answer is: ", k)
print("Probability of certainty was: ", pred_results[0][val_max])
# Predicted answer is: no
# Probability of certainty was: 0.99999964
Conclusion
The work done describes the use of neural networks to train a chat bot. Following the creation of the model, test is carried out on the model, with very impressive accuracy of prediction of the results. The Facebook bAbi dataset proved very helpful and instrumental for this research.
References
artificial-solutions.com/chatbots (2020) ‘Chatbots: The definitive guide’.
Bhowmick .H(2019).‘Your chatbot is cool — but how does it work’?
You can find the link to paper and code reference here.
Dialog-based Language Learning dataset
More information about Keras Layers can be found here.